The Bonding in Gaseous Hydrogen Halides Is Best Described as
Can someone please explain why the bonding in gaseous hydrogen halides is best described as mainly covalent with an increasing tendency towards ionic as you go up the group. Again due to the presence of hydrogen bonds in Hydrogen Fluoride HF molecule its melting and boiling points are higher.
Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides Chemistry Libretexts
The shape of the triiodide ion I 3-1 is best described as.

. At I atm and 298 K pentane C5H12 is a liquid but propane C3H8 is a gas. Hydrogen bonds also occur when hydrogen is bonded to fluorine but the HF group does not appear in other molecules. An alcohol is an organic molecule containing an -OH group.
The best explanation for this is. The bonds in pentane are stronger than the CH bonds in propane. HF pKa 31 HCl pKa -60 HBr pKa -90 HI pKa -95.
A molecular solid with hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding in ethanol. Report Thread starter 9 years ago.
Can someone please explain why the bonding in gaseous hydrogen halides is best described as mainly covalent with an increasing tendency towards ionic as you go up the group. Hydrogen chloride gas has a smaller molar volume than predicted by the Ideal Gas Law. Which of the following describes hydrogen bonding.
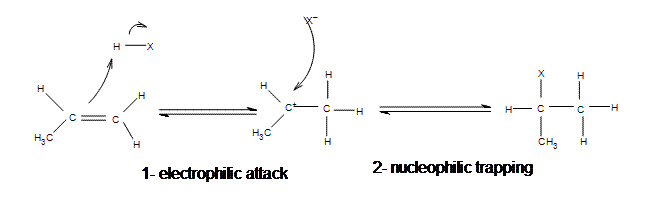
What type of macromolecule is often referred to. When the hydrogen halides react with alkenes the hydrogen-halogen bond has to be broken. Which intermolecular forces exist in dry ice CO 2 s.
This difference in boiling points may be attributed to a difference in. Based on concepts of polarity and hydrogen bonding which of the following. Because it is difficult to break the bond between the hydrogen and the fluorine the addition of HF is bound to be slow.
HI HBr HCl HF as H-X bond strength of HI HBr HCl HF The pka value of the given halides are. The bond strength falls as you go from HF to HI and the hydrogen-fluorine bond is particularly strong. The Interaction of Dihalogens and Hydrogen Halides with Lewis Bases in the Gas Phase.
This is clearly demonstrated by the gradual decrease of melting and boiling points of Hydrogen halides Hf HCl HBr HI. PK a -log K a The order of acidic strength of hydrogen halides are. The liquefied hydrogen halides have the normal boiling points given above The relatively high boiling point of HF can be correctly explained by which of the following.
The relatively high boiling point of HF can be correctly explained by which of the following. An Experimental Comparison of the Halogen Bond and the Hydrogen Bond September 2007 Structure and Bonding 126. Any molecule which has a hydrogen atom attached directly to an oxygen or a nitrogen is capable of hydrogen bonding.
A HF gas is more ideal. D HF is much less soluble in water. CH bonds in pentane are weaker than the CH bonds in propane.
Which statement is incorrect about the hydrogen halides. This further down you go the less the difference in electronegativity and the more covalent. The hydrogen bonds is an intermolecular force.
This is it is an atracction among molecules which trends to keep the molecules close one to each other quite strongly. A network solid with covenant bonding. Hence HF has the highest pKa value.
Interactions between positive and negative regions of polar molecules. E HF molecules tend to form. The liquefied hydrogen halides have the normal boiling points given above.
Up to 24 cash back 7. Van der Waals forces D. The geometry and bond angle of the sulfite ion.
The forces among pentane molecules are stronger than those among propane molecules. Vaporization is the pass from liquid where the molecules are pretty close one to each other to gas where the molecules are more distant from each other. CH3CH2OH boils at 78 C and CH3OCH3 boils at - 24 C although both compounds have the same composition.
C HF molecules have a smaller dipole moment. Fluorine has a higher electronegativity than the other halogens which means for fluorine it undergoes hydrogen bonding which gives. The hydrogen halides are HF HCl HBr HI.
Interactions between positive and negative regions of non-polar molecules. In water the hydrohalic acids are formed by reaction with the gaseous hydrogen halides and apart from HF these are completely dissociating strong acids. Hydrogen bonding exists between the molecules in which hydrogen is covalently bonded with a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen oxygen and fluorine.
B HF is the strongest acid. Due to the large difference in the electronegativity of the atoms partial positive charge develops on the hydrogen atom and partial negative charge develops on the electronegative atom. A bond formed between donated electrons.
In the case of HF where there is a short strong bond bond dissociation energy of 570 kJ mol. A Each gaseous HX molecule is polar b All are gases at 298 K c Bond dissociation energies for Hx decrease down the group d For each HX the pka value is negative indicating that each is a strong acid Anar. Using reference table bond enthalpy of C double bond C is 610kJmol while H-H bond is 436kJmol.
Hydrogen bonding in alcohols. Most hydrogen bonds are best described as electrostatic interactions between a hydrogen atom bound to an electronegative atom and another atom that is also electronegative Ah and has one or more lone pairs enabling it to act as a base. Up to 10 cash back Our work in Exeter on hydrogen-bonded complexes between 1984 and 1993 culminated in a series of detailed studies of the ammonium and methylammonium halides in the gas phase whose aim was to discover whether the extent of proton transfer from HX to the amine subunit in gas-phase complexes such as H 3 NHCl.
Calculate the energy required to break C-C double bond and H-H bond and addition of this gives the total amount of energy required to break the desired bonds in propene and hydrogen gas that is 1046kJmol610kJmol 436 Kjmol 1046 kJmol. It means the hydrogen - halogen bond.
The Chemistry Of The Halogens 3
What Type Of Bonding Is Shown By Hydrogen Halides Quora

Halogens Edexcel New Specification Application Of Core Principles Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment